Cesium-137 (Cs-137) is a remarkable isotope with diverse applications in various fields. In this post, I’ll explore how Cs-137 is produced, its critical industrial roles, and its significance in gamma spectroscopy.

What is Cesium-137?
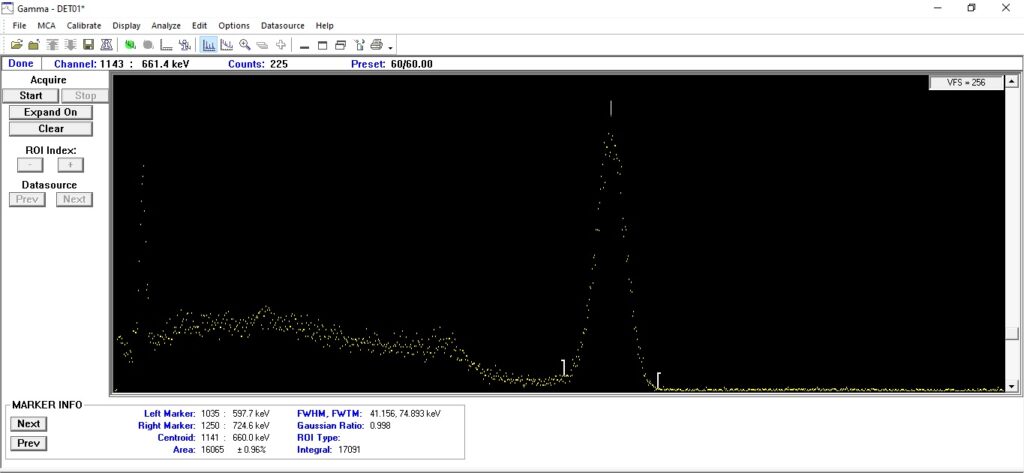
Cesium-137 is a radioactive isotope of cesium with a half-life of about 30.17 years. It decays via beta decay to metastable barium-137m (Ba-137m), which then decays to stable barium-137 (Ba-137) by emitting gamma radiation. The primary gamma photon produced has an energy of 662 keV, making Cs-137 a potent source of gamma rays.
How is Cesium-137 Produced?
Cs-137 is not found naturally but is produced through nuclear fission of uranium-235 (U-235) and plutonium-239 (Pu-239) in nuclear reactors. During the fission process, a variety of fission products are created, including Cs-137. The steps involved in the production are:
- Nuclear Fission: U-235+n→Fission Products (including Cs-137)
- Separation and Purification: After the fission reaction, Cs-137 is chemically separated and purified from other fission products for use in various applications.
Industrial Applications of Cesium-137
Cs-137 has several crucial industrial applications due to its gamma radiation and relatively long half-life:
- Medical Radiotherapy: Cs-137 is used in brachytherapy, a type of radiotherapy where a sealed radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. It’s particularly effective in treating certain types of cancer.
- Industrial Gauges: Cs-137 is used in industrial gauging applications to measure the thickness, density, or composition of materials. Its gamma rays penetrate materials, and the absorption levels help determine the desired properties.
- Environmental Monitoring: Cs-137 is used to study soil erosion and sediment movement. Its presence in soil layers acts as a marker to trace soil displacement and accumulation patterns.
- Security and Safety: Cs-137 is utilized in security devices, such as radiation detection instruments as a known energy calibration source. That’s mandatory to calibrate the instrument for measuring radiation levels.
Cesium-137 in Gamma Spectroscopy
Gamma spectroscopy involves analyzing the energy and intensity of gamma rays emitted by radioactive substances. Cs-137 is a widely used calibration source in gamma spectroscopy due to its strong and well-defined gamma emission at 662 keV.
In gamma spectroscopy, Cs-137 provides a reliable standard for calibrating detectors and ensuring the accurate measurement of gamma radiation.